Question 5:
Solution:
(a)
(b)
(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
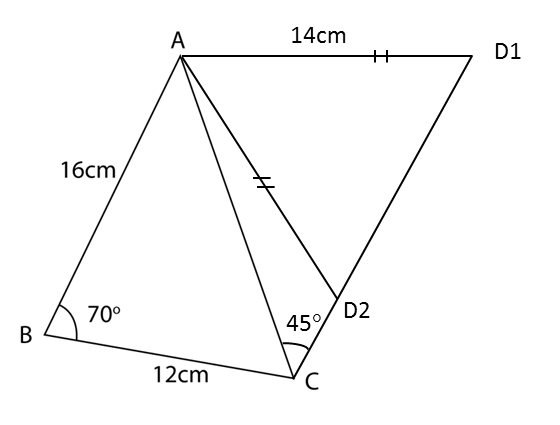
The diagram below shows a triangle ABC.
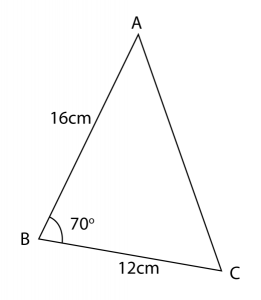

(a) Calculate the length, in cm, of AC.
(b) A quadrilateral ABCD is now formed so that AC is a diagonal, ∠ACD = 45° and AD = 14 cm. Calculate the two possible values of ∠ADC.
(c) By using the acute ∠ADC from (b), calculate
(i) the length, in cm, of CD,
(ii) the area, in cm2, of the quadrilateral ABCD
Solution:
(a)
Using cosine rule,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2 – 2 (AB)(BC) ∠ABC
AC2 = 162 + 122 – 2 (16)(12) cos 70o
AC2 = 400 – 131.33
AC2 = 268.67
AC = 16.39 cm
(b)

(c)(i)
(c)(ii)
Question 6:
Diagram below shows trapezium ABCD.
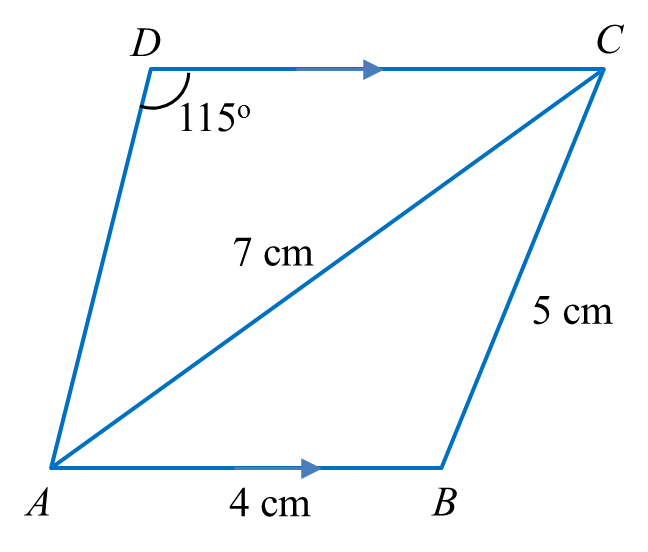 (a) Calculate
(a) Calculate
(i) ∠BAC.
(ii) the length, in cm, of AD.
(b) The straight line AB is extended to B’ such that BC = B’C.
(i) Sketch the trapezium AB’CD.
(ii) Calculate the area, in cm2, of ∆BB’C.
Solution:
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
(b)(i)
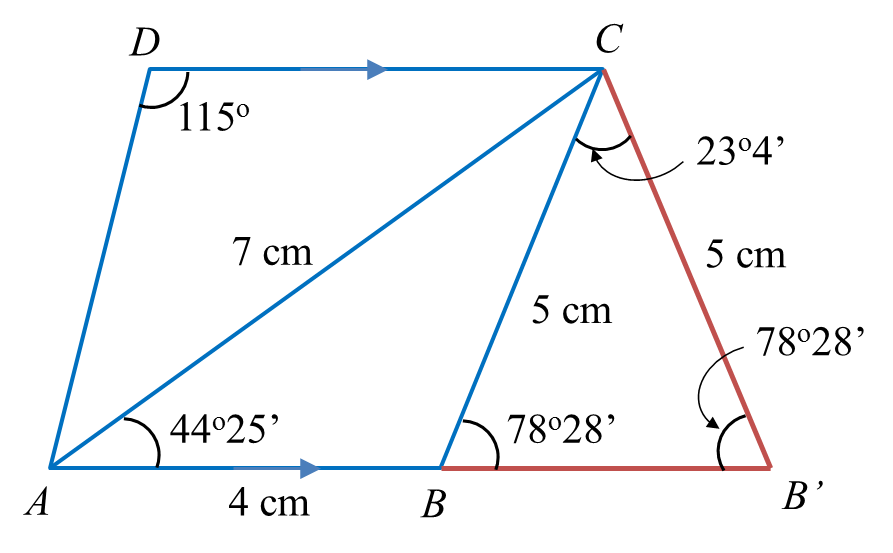
(b)(ii)
Diagram below shows trapezium ABCD.
 (a) Calculate
(a) Calculate(i) ∠BAC.
(ii) the length, in cm, of AD.
(b) The straight line AB is extended to B’ such that BC = B’C.
(i) Sketch the trapezium AB’CD.
(ii) Calculate the area, in cm2, of ∆BB’C.
Solution:
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
(b)(i)

(b)(ii)