Question 1:
Solution:
BD = 6.013 cm
(c)
Using sine rule,
(d)
Area of quadrilateral ABCD

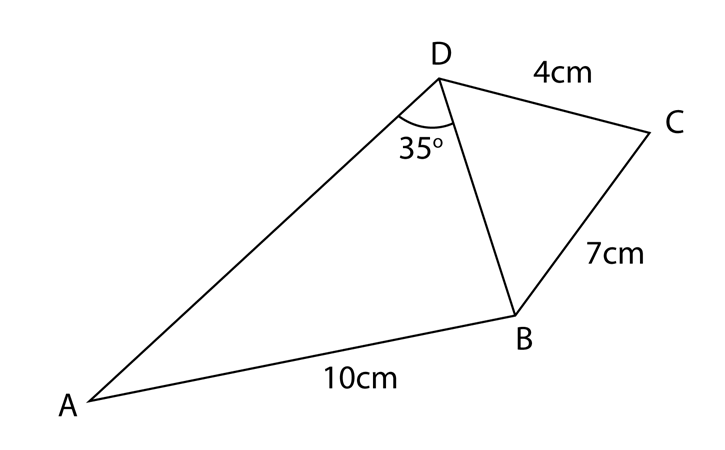
The diagram shows a quadrilateral ABCD. The area of triangle BCD is 12 cm2 and ∠BCD is acute. Calculate
(a) ∠BCD,
(b) the length, in cm, of BD,
(c) ∠ABD,
(d) the area, in cm2, quadrilateral ABCD.
Solution:
(a) Given area of triangle BCD = 12 cm2
½ (BC)(CD) sin C = 12
½ (7) (4) sin C = 12
14 sin C = 12
sin C = 12/14 = 0.8571
C = 59o
∠BCD = 59o
(b)
Using cosine rule,
Using cosine rule,
BD2 = BC2 + CD2 – 2 (7)(4) cos 59o
BD2 = 72+ 42 – 2 (7)(4) cos 59o
BD2 = 65 – 28.84
BD2 = 36.16
BD = 36.16 BD = 6.013 cm
(c)
Using sine rule,
(d)
Area of quadrilateral ABCD
= Area of triangle ABD + Area of triangle BCD
= ½ (AB)(BD) sin B + 12 cm
= ½ (10) (6.013) sin 124.82 + 12
= 24.68 + 12
= 36.68 cm²
Question 2:
It is given that BG= 40cm, GA = 33 cm, AH = 30 cm, GAH = 85o and JBK= 45o.
Solution:
(a)(i)
(b)
(c)
In the diagram below, ABC is a triangle. AGJB, AHC and BKC are straight lines. The straight line JK is perpendicular to BC.
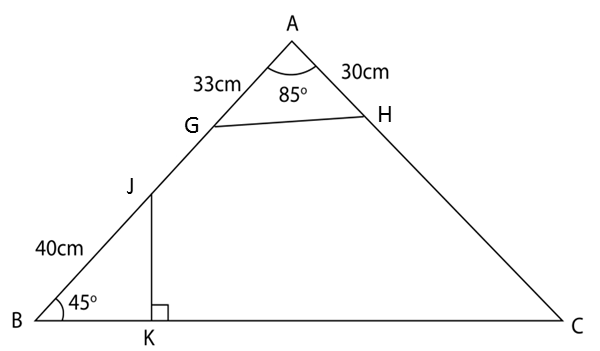

It is given that BG= 40cm, GA = 33 cm, AH = 30 cm, GAH = 85o and JBK= 45o.
(a) Calculate the length, in cm of
i. GH
ii. HC
(b) The area of triangle GAH is twice the area of triangle JBK. Calculate the length, in cm,
of BK.
(c) Sketch triangle which has a different shape from triangle ABC such that, A’B’ = AB,
A’C’ = AC and ∠A’B’C’ = ∠ABC.
(a)(i)
Using cosine rule,
GH2 = AG2 + AH2 – 2 (AG)(AH) ∠GAH
GH2 = 332+ 302 – 2 (33)(30) cos 85o
GH2 = 1089 + 900 – 172.57
GH2 = 1816.43
GH = 42.62 cm
(a)(ii)
(b)
(c)
