Question 4:
$$ \text { Diagram } 3 \text { shows point A lies on the circumference of a unit circle. } $$
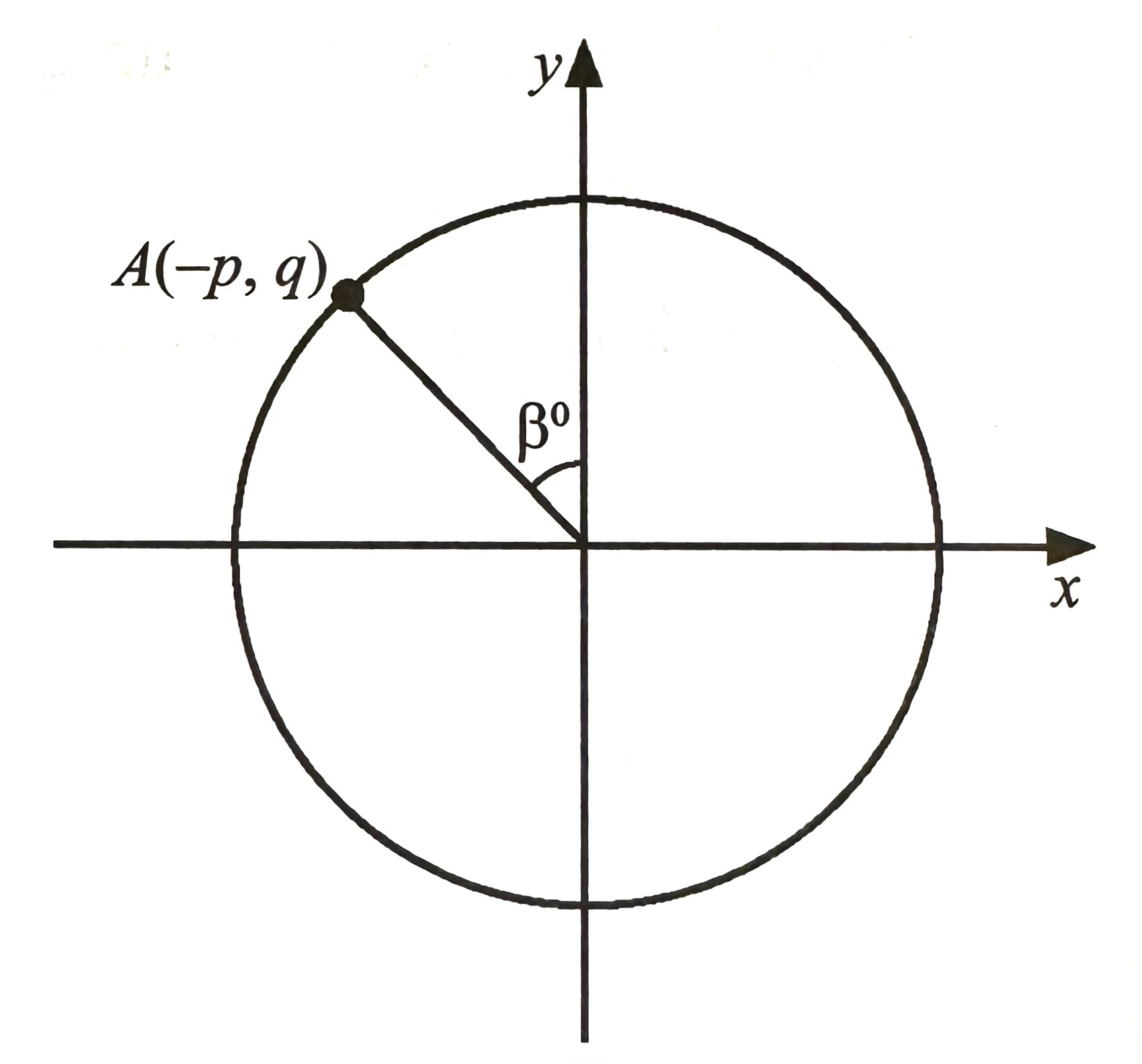 Express in terms of p and / or q of.
Express in terms of p and / or q of.
(a) tan β,
(b) cot (180o + β)
[2 marks]
Solution:
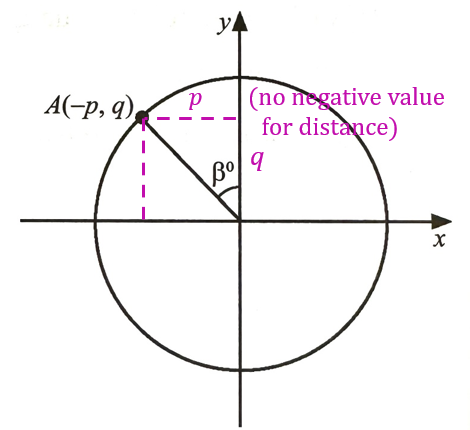
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} \tan \beta & =\frac{\text { Opposite }}{\text { Adjacent }}(\mathrm{TOA}) \\ \tan \beta & =\frac{p}{q} \end{aligned} $$
(b)
$$ \begin{aligned} &\tan (A+B)=\frac{\tan A+\tan B}{1-\tan A \tan B}\\ &\begin{aligned} \cot \left(180^{\circ}+\beta\right) & =\frac{1}{\tan \left(180^{\circ}+\beta\right)} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{\tan 180^{\circ}+\tan \beta}{1-\tan 180^{\circ} \tan \beta}} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{0+\tan \beta}{1-(0) \tan \beta}} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{\tan \beta}{1}} \\ & =\frac{1}{\tan \beta} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{p}{q}} \\ & =\frac{q}{p} \end{aligned} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \text { Diagram } 3 \text { shows point A lies on the circumference of a unit circle. } $$
 Express in terms of p and / or q of.
Express in terms of p and / or q of.(a) tan β,
(b) cot (180o + β)
[2 marks]
Solution:

(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} \tan \beta & =\frac{\text { Opposite }}{\text { Adjacent }}(\mathrm{TOA}) \\ \tan \beta & =\frac{p}{q} \end{aligned} $$
(b)
$$ \begin{aligned} &\tan (A+B)=\frac{\tan A+\tan B}{1-\tan A \tan B}\\ &\begin{aligned} \cot \left(180^{\circ}+\beta\right) & =\frac{1}{\tan \left(180^{\circ}+\beta\right)} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{\tan 180^{\circ}+\tan \beta}{1-\tan 180^{\circ} \tan \beta}} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{0+\tan \beta}{1-(0) \tan \beta}} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{\tan \beta}{1}} \\ & =\frac{1}{\tan \beta} \\ & =\frac{1}{\frac{p}{q}} \\ & =\frac{q}{p} \end{aligned} \end{aligned} $$
Question 5:
$$ \text { Diagram } 4 \text { shows three points on a Cartesian plane. } $$
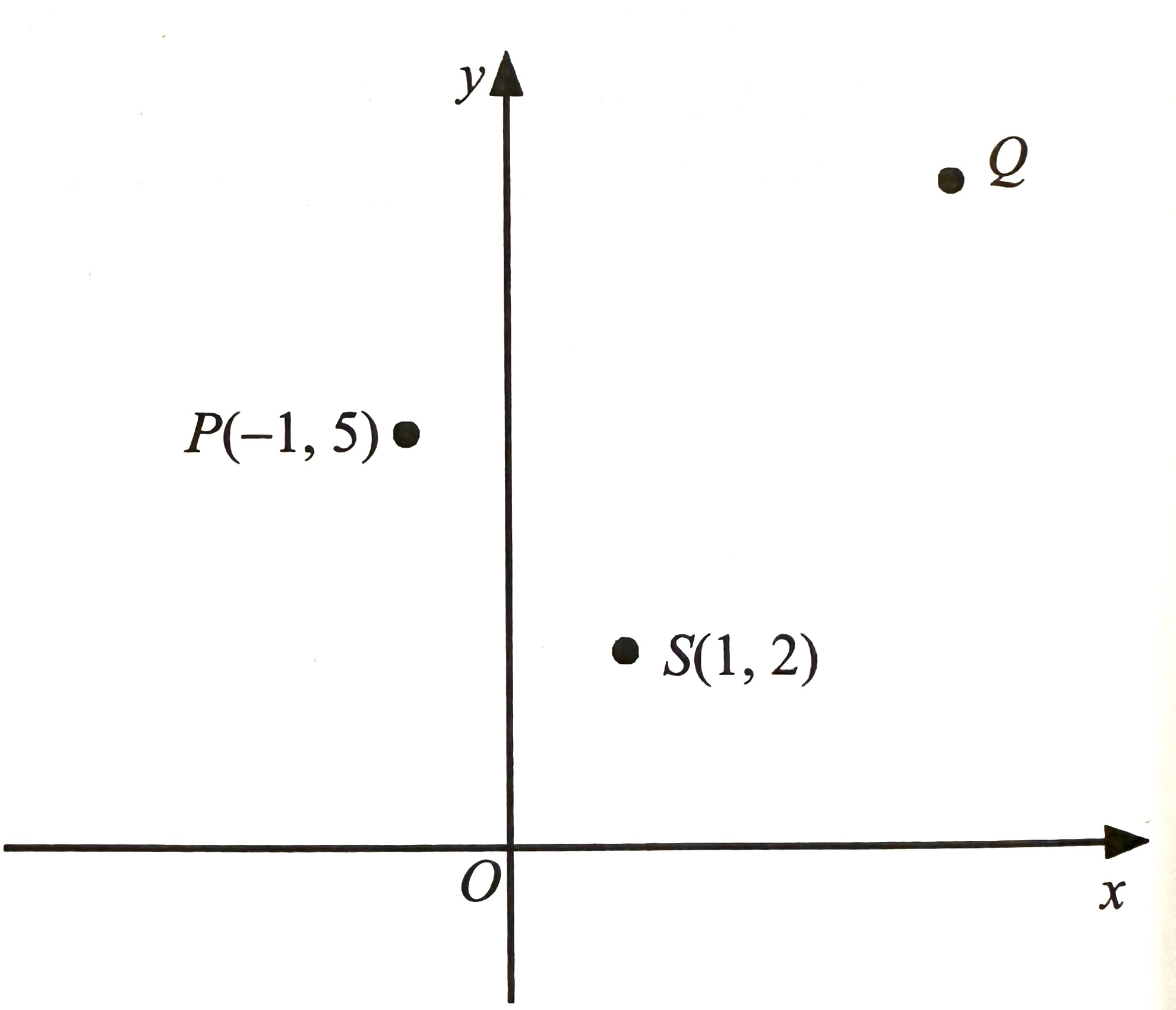 $$
\text { (a) State } \overrightarrow{S P} \text { [1 mark]. }
$$
$$
\text { (a) State } \overrightarrow{S P} \text { [1 mark]. }
$$
$$ \text { (b) It is given that } \overrightarrow{P Q}=5 \underline{i}+m \underline{j} \text {. } $$
$$ \text { (i) If } \overrightarrow{S P}+3 \overrightarrow{P Q}=13 \underline{i}+15 j \text {, find the value of } m \text { by using vector’s }\text { arithmetic operations } $$
$$ \text { (ii) Hence, determine the unit vector in the direction of } \overrightarrow{P Q} \text {. } $$
[4 marks]
Solution:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{S P} & =\overrightarrow{S O}+\overrightarrow{O P} \\ & =-(i+2 \underset{\sim}{j})+(-i+5 \underset{\sim}{j}) \\ & =-i -2\underset{\sim}{j}-\underset{\sim}{i}+5 \underset{\sim}{j} \\ & =-2 \underset{\sim}{i}+3 \underset{\sim}{j} \end{aligned} $$
(b)(i)
$$ \begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{S P}+3 \overrightarrow{P Q} & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \\ (-2 \underline{i}+3 \underline{j})+3(5 \underline{i}+m \underline{j}) & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \\ -2 \underline{i}+3 \underline{j}+15 \underline{i}+3 m \underline{j}) & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \\ 13 \underline{i}+(3 m+3) \underline{j} & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 3 m+3 & =15 \\ 3 m & =12 \\ m & =4 \end{aligned} $$
(b)(ii)
$$ \begin{aligned} & \overrightarrow{P Q}=5 \underline{i}+4 \underline{j} \\ & |\overrightarrow{P Q}|=\sqrt{5^2+4^2} \\ & |\overrightarrow{P Q}|=\sqrt{41} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \text { Unit vector }=\frac{5 \underline{i}+4 \underline{j}}{\sqrt{41}} $$
$$ \text { Diagram } 4 \text { shows three points on a Cartesian plane. } $$
 $$
\text { (a) State } \overrightarrow{S P} \text { [1 mark]. }
$$
$$
\text { (a) State } \overrightarrow{S P} \text { [1 mark]. }
$$$$ \text { (b) It is given that } \overrightarrow{P Q}=5 \underline{i}+m \underline{j} \text {. } $$
$$ \text { (i) If } \overrightarrow{S P}+3 \overrightarrow{P Q}=13 \underline{i}+15 j \text {, find the value of } m \text { by using vector’s }\text { arithmetic operations } $$
$$ \text { (ii) Hence, determine the unit vector in the direction of } \overrightarrow{P Q} \text {. } $$
[4 marks]
Solution:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{S P} & =\overrightarrow{S O}+\overrightarrow{O P} \\ & =-(i+2 \underset{\sim}{j})+(-i+5 \underset{\sim}{j}) \\ & =-i -2\underset{\sim}{j}-\underset{\sim}{i}+5 \underset{\sim}{j} \\ & =-2 \underset{\sim}{i}+3 \underset{\sim}{j} \end{aligned} $$
(b)(i)
$$ \begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{S P}+3 \overrightarrow{P Q} & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \\ (-2 \underline{i}+3 \underline{j})+3(5 \underline{i}+m \underline{j}) & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \\ -2 \underline{i}+3 \underline{j}+15 \underline{i}+3 m \underline{j}) & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \\ 13 \underline{i}+(3 m+3) \underline{j} & =13 \underline{i}+15 \underline{j} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} 3 m+3 & =15 \\ 3 m & =12 \\ m & =4 \end{aligned} $$
(b)(ii)
$$ \begin{aligned} & \overrightarrow{P Q}=5 \underline{i}+4 \underline{j} \\ & |\overrightarrow{P Q}|=\sqrt{5^2+4^2} \\ & |\overrightarrow{P Q}|=\sqrt{41} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \text { Unit vector }=\frac{5 \underline{i}+4 \underline{j}}{\sqrt{41}} $$