2.6 Gradients of Tangents, Equations of Tangents and Normals
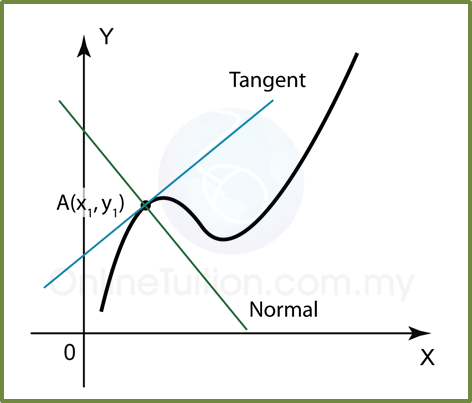

If A(x1, y1) is a point on a line y = f(x), the gradient of the line (for a straight line) or the gradient of the tangent of the line (for a curve) is the value of
when x = x1.
(A) Gradient of tangent at A(x1, y1):


(B) Equation of tangent:

(C) Gradient of normal at A(x1, y1):
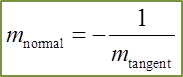

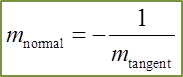

(D) Equation of normal :

Example 1 (Find the Equation of Tangent)
Given that
. Find the equation of the tangent at the point (1, 1).
Solution:
Example 2 (Find the Equation of Normal)
Solution:
Find the gradient of the curve
at the point (-1, 7). Hence, find the equation of the normal to the curve at this point.
Solution: