Question 5:
Solution:

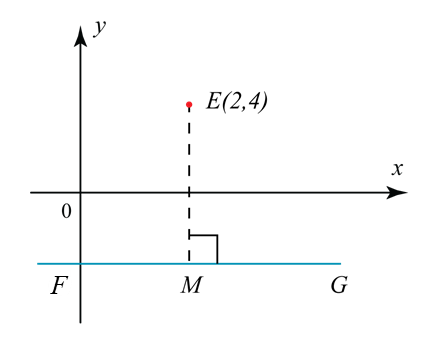
In the diagram, the equation of FMG is y = – 4. A point P moves such that its distance from E is always half of the distance of E from the straight line FG. Find
(a) The equation of the locus of P,
(b) The x-coordinate of the point of intersection of the locus and the x-axis.
Solution:
(a)
Gradient of the straight line FMG = 0
EM is perpendicular to FMG, so gradient of EM also = 0, equation of EM is x = 2
Thus, coordinates of point M = (2, –4).
Let coordinates of point P = (x, y).
Given PE = ½ EM
2PE = EM
2 [(x – 2)2+ (y – 4)2]½ = [(2 – 2)2 + (4 – (–4))2]½
4 (x2 – 4x + 4 + y2 – 8y +16) = (0 + 64) → (square for both sides)
4x2 – 16x + 16 + 4y2 – 32y + 64 = 64
4x2 + 4y2 – 16x – 32y + 16 = 0
x2 + y2 – 4x – 8y + 4 = 0
(b)
x2 + y2 – 4x – 8y + 4 = 0
At x axis, y = 0.
x2 + 0 – 4x – 8(0) + 4 = 0
x2 – 4x+ 4 = 0
(x – 2) (x – 2) = 0
x = 2
The x-coordinate of the point of intersection of the locus and the x-axis is 2.
Question 6:
Solutions by scale drawing will not be accepted.
Diagram below shows a triangle PRS. Side PR intersects the y-axis at point Q.
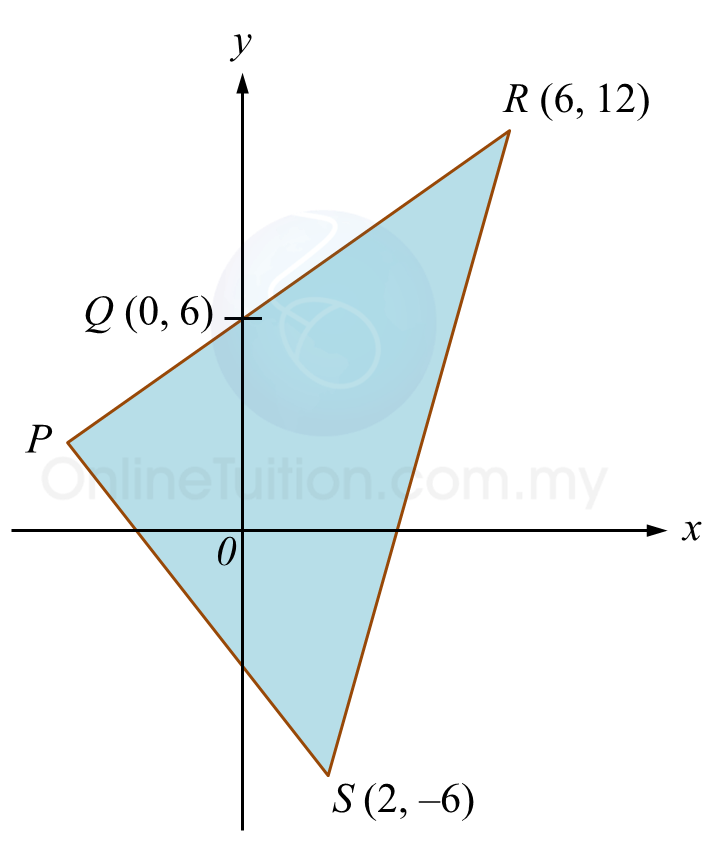
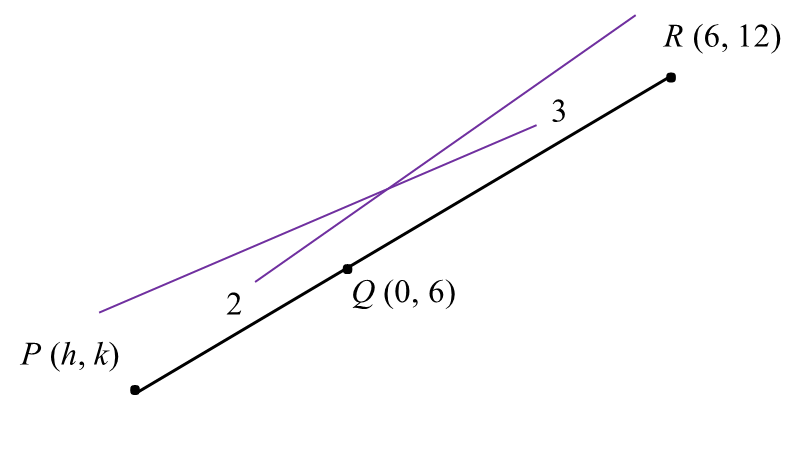
(a) Given PQ : QR = 2 : 3, find
(i) The coordinates of P,
(ii) The equation of the straight line PS,
(iii) The area, in unit2, of triangle PRS.
(b) Point M moves such that its distance from point R is always twice its distance from point S.
Find the equation of the locus M.
Solution:
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
(a)(iii)
(b)
Solutions by scale drawing will not be accepted.
Diagram below shows a triangle PRS. Side PR intersects the y-axis at point Q.

(a) Given PQ : QR = 2 : 3, find
(i) The coordinates of P,
(ii) The equation of the straight line PS,
(iii) The area, in unit2, of triangle PRS.
(b) Point M moves such that its distance from point R is always twice its distance from point S.
Find the equation of the locus M.
Solution:
(a)(i)

(a)(ii)
(a)(iii)
(b)