Question 5:
It is given that (2x + 3) is one of the factors of f(x) = x (5 – 2x) + m, such that m is a constant.
(a) Find the value of m. [3 marks]
(b) By using the method of completing the square, express f(x) in the form, f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k, such that a, h and k are constants.
Hence, sketch the graph of f(x) for 0 ⩽ x ⩽ 4.
[4 marks]
(c) Using the same axes in (b), sketch and label the graph of g(x) = (a – 1)(x – h)2 + k.
[1 mark]
Solution:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} 2 x+3 & =0 \\ 2 x & =-3 \\ x & =-\frac{3}{2} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} & f(x)=x(5-2 x)+m \\ & f(x)=5 x-2 x^2+m \\ & f(x)=-2 x^2+5 x+m \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { When } x=-\frac{3}{2}, f(x)=0 \\ & \begin{aligned} -2\left(-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2+5\left(-\frac{3}{2}\right)+m & =0 \\ -12+m & =0 \\ m & =12 \end{aligned} \end{aligned} $$
(b)
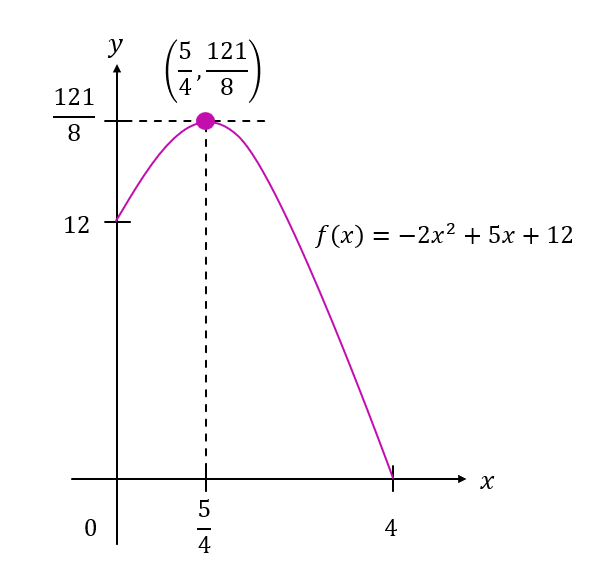
$$ \begin{aligned} f(x) & =-2 x^2+5 x+12 \\ & =-2\left(x^2-\frac{5}{2} x-6\right) \\ & =-2\left[x^2-\frac{5}{2} x+\left(\frac{-\frac{5}{2}}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{-\frac{5}{2}}{2}\right)^2-6\right] \\ & =-2\left[x^2-\frac{5}{2} x+\left(-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-\left(-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-6\right] \\ & =-2\left[\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-\frac{25}{16}-6\right] \\ & =-2\left[\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-\frac{121}{16}\right] \\ & =-2\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ \therefore a & =-2, h=\frac{5}{4}, k=\frac{121}{8} \end{aligned} $$
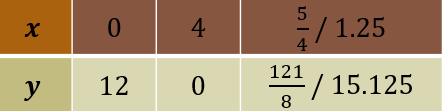
$$ \begin{aligned} \text { When } x & =0 \\ f(x) & =12 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} &\text { When } f(x)=0\\ &\begin{aligned} -2 x^2+5 x+12 & =0 \\ 2 x^2-5 x-12 & =0 \\ (x-4)(2 x+3) & =0 \\ x=4, \quad x= & -\frac{3}{2} \text { (ignore) } \end{aligned} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} &\text { From } f(x)=-2\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8}\\ &\text { Turning point }=\left(\frac{5}{4}, \frac{121}{8}\right)=(1.25,15.125) \end{aligned} $$
(c)
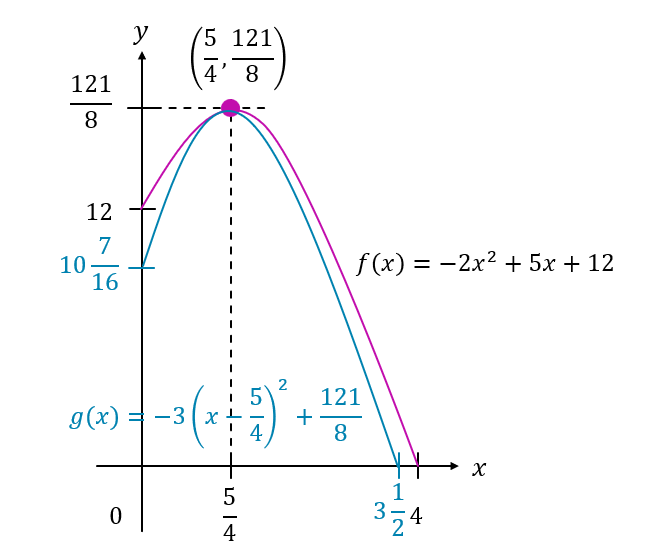
$$ \begin{aligned} g(x) & =(a-1)(x-h)^2+k \\ & =(-2-1)\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ & =-3\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \end{aligned} $$
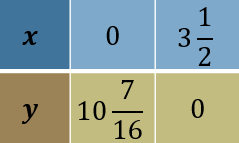
$$ \begin{aligned} \text { When } x & =0 \\ g(x) & =-3\left(0-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ & =10 \frac{7}{16} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { When } g(x)=0 \\ & 0=-3\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ & 3\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2=\frac{121}{8} \\ & \left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)= \pm \sqrt{\frac{121}{24}} \\ & x= \pm \sqrt{\frac{121}{24}}+\frac{5}{4} \\ & x=3.5, \quad 1 \text { (ignore) } \end{aligned} $$
It is given that (2x + 3) is one of the factors of f(x) = x (5 – 2x) + m, such that m is a constant.
(a) Find the value of m. [3 marks]
(b) By using the method of completing the square, express f(x) in the form, f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k, such that a, h and k are constants.
Hence, sketch the graph of f(x) for 0 ⩽ x ⩽ 4.
[4 marks]
(c) Using the same axes in (b), sketch and label the graph of g(x) = (a – 1)(x – h)2 + k.
[1 mark]
Solution:
(a)
$$ \begin{aligned} 2 x+3 & =0 \\ 2 x & =-3 \\ x & =-\frac{3}{2} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} & f(x)=x(5-2 x)+m \\ & f(x)=5 x-2 x^2+m \\ & f(x)=-2 x^2+5 x+m \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { When } x=-\frac{3}{2}, f(x)=0 \\ & \begin{aligned} -2\left(-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2+5\left(-\frac{3}{2}\right)+m & =0 \\ -12+m & =0 \\ m & =12 \end{aligned} \end{aligned} $$
(b)
$$ \begin{aligned} f(x) & =-2 x^2+5 x+12 \\ & =-2\left(x^2-\frac{5}{2} x-6\right) \\ & =-2\left[x^2-\frac{5}{2} x+\left(\frac{-\frac{5}{2}}{2}\right)^2-\left(\frac{-\frac{5}{2}}{2}\right)^2-6\right] \\ & =-2\left[x^2-\frac{5}{2} x+\left(-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-\left(-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-6\right] \\ & =-2\left[\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-\frac{25}{16}-6\right] \\ & =-2\left[\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2-\frac{121}{16}\right] \\ & =-2\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ \therefore a & =-2, h=\frac{5}{4}, k=\frac{121}{8} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} \text { When } x & =0 \\ f(x) & =12 \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} &\text { When } f(x)=0\\ &\begin{aligned} -2 x^2+5 x+12 & =0 \\ 2 x^2-5 x-12 & =0 \\ (x-4)(2 x+3) & =0 \\ x=4, \quad x= & -\frac{3}{2} \text { (ignore) } \end{aligned} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} &\text { From } f(x)=-2\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8}\\ &\text { Turning point }=\left(\frac{5}{4}, \frac{121}{8}\right)=(1.25,15.125) \end{aligned} $$


(c)
$$ \begin{aligned} g(x) & =(a-1)(x-h)^2+k \\ & =(-2-1)\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ & =-3\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} \text { When } x & =0 \\ g(x) & =-3\left(0-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ & =10 \frac{7}{16} \end{aligned} $$
$$ \begin{aligned} & \text { When } g(x)=0 \\ & 0=-3\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2+\frac{121}{8} \\ & 3\left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)^2=\frac{121}{8} \\ & \left(x-\frac{5}{4}\right)= \pm \sqrt{\frac{121}{24}} \\ & x= \pm \sqrt{\frac{121}{24}}+\frac{5}{4} \\ & x=3.5, \quad 1 \text { (ignore) } \end{aligned} $$

