Question 11:
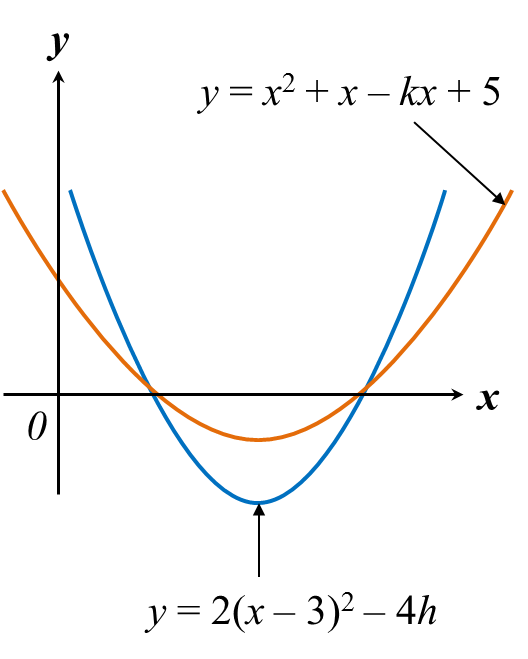
Diagram above shows the graphs of the curves y = x2 + x – kx + 5 and y = 2(x – 3) – 4h that intersect the x-axis at two points. Find
(a) the value of k and of h,
(b) the minimum value of each curve.
Solution:
(a)
(b)

Diagram above shows the graphs of the curves y = x2 + x – kx + 5 and y = 2(x – 3) – 4h that intersect the x-axis at two points. Find
(a) the value of k and of h,
(b) the minimum value of each curve.
Solution:
(a)
(b)
Question 12:
Quadratic function f(x) = x2 – 4px + 5p2 + 1 has a minimum value of m2 + 2p, where m and p are constants.
(a) By using the method of completing the square, shows that m = p – 1.
(b) Hence, find the values of p and of m if the graph of the quadratic function is symmetry at x = m2 – 1.
Solution:
(a)
(b)
Quadratic function f(x) = x2 – 4px + 5p2 + 1 has a minimum value of m2 + 2p, where m and p are constants.
(a) By using the method of completing the square, shows that m = p – 1.
(b) Hence, find the values of p and of m if the graph of the quadratic function is symmetry at x = m2 – 1.
Solution:
(a)
(b)
Question 13 (SPM 2009):
The quadratic equation x2 – 5x + 6 = 0 has roots h and k, where h > k.
(a) Find
(i) the value of h and of k.
(ii) the range of x if x2 – 5x + 6 > 0.
[5 marks]
(b) Using the values of h and k from 2(a)(i), form the quadratic equation which has roots h + 2 and 3k – 2.
[2 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
$$ \begin{aligned} &\begin{array}{r} x^2-5 x+6=0 \\ (x-2)(x-3)=0 \\ x=2 \text { or } x=3 \end{array}\\ &\text { Since } h>k, h=3 \text { and } k=2 \text {. } \end{aligned} $$
(a)(ii)
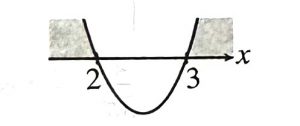
$$ \begin{array}{r} x^2-5 x+6>0 \\ (x-2)(x-3)>0 \end{array} $$ The range is x < 2 or x > 3.
(b)
$$ \begin{aligned} &\begin{aligned} & h+2=3+2=5 \\ & 3 k-2=3(2)-2=4 \end{aligned}\\ &\text { The quadratic equation is }\\ &\begin{array}{r} x^2-(5+4) x+5(4)=0 \\ x^2-9 x+20=0 \end{array} \end{aligned} $$
The quadratic equation x2 – 5x + 6 = 0 has roots h and k, where h > k.
(a) Find
(i) the value of h and of k.
(ii) the range of x if x2 – 5x + 6 > 0.
[5 marks]
(b) Using the values of h and k from 2(a)(i), form the quadratic equation which has roots h + 2 and 3k – 2.
[2 marks]
Answer:
(a)(i)
$$ \begin{aligned} &\begin{array}{r} x^2-5 x+6=0 \\ (x-2)(x-3)=0 \\ x=2 \text { or } x=3 \end{array}\\ &\text { Since } h>k, h=3 \text { and } k=2 \text {. } \end{aligned} $$
(a)(ii)
$$ \begin{array}{r} x^2-5 x+6>0 \\ (x-2)(x-3)>0 \end{array} $$ The range is x < 2 or x > 3.

(b)
$$ \begin{aligned} &\begin{aligned} & h+2=3+2=5 \\ & 3 k-2=3(2)-2=4 \end{aligned}\\ &\text { The quadratic equation is }\\ &\begin{array}{r} x^2-(5+4) x+5(4)=0 \\ x^2-9 x+20=0 \end{array} \end{aligned} $$