Example
By taking into consideration the ambiguous case. Solve ∆ABC such that c = 6cm, a = 5cm and ∠A = 40°
Answer:
Step 1: To prove whether this is an ambiguous case/non-ambiguous case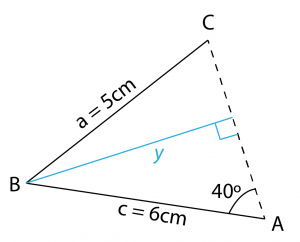 \[\begin{gathered}
\[\begin{gathered}
\sin {40^o} = \frac{y}{6} \hfill \\
y = 6\sin {40^o} \hfill \\
y = 3.857cm \hfill \\
\end{gathered} \]
y < a < c
Therefore, this is an ambiguous case. There are 2 solutions for the triangle.
Step 2: Solve Case 1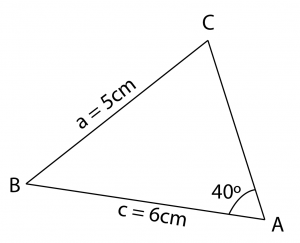 To find angle C
To find angle C
\[\begin{gathered}
\frac{{\sin A}}{a} = \frac{{\sin C}}{c} \hfill \\
\frac{{\sin {{40}^o}}}{5} = \frac{{\sin C}}{6} \hfill \\
\sin C = \frac{{\sin {{40}^o}}}{5} \times 6 \hfill \\
\sin C = 0.7713 \hfill \\
C = {50.47^o} \hfill \\
\end{gathered} \]
To find angle B
\[\begin{gathered}
B = {180^o} – {40^o} – {50.47^o} \hfill \\
B = {89.53^o} \hfill \\
\end{gathered} \]
To find length of side b
\[\begin{gathered}
\frac{b}{{\sin B}} = \frac{a}{{\sin A}} \hfill \\
\frac{b}{{\sin 89.53}} = \frac{5}{{\sin 40}} \hfill \\
b = \frac{5}{{\sin 40}} \times \sin 89.53 \hfill \\
b = 7.778cm \hfill \\
\end{gathered} \]
Step 3: Solve Case 2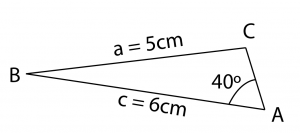 To find Angle C
To find Angle C
\[\begin{gathered}
\frac{{\sin A}}{a} = \frac{{\sin C}}{c} \hfill \\
\frac{{\sin {{40}^o}}}{5} = \frac{{\sin C}}{6} \hfill \\
\sin C = \frac{{\sin {{40}^o}}}{5} \times 6 \hfill \\
\sin C = 0.7713 \hfill \\
C = {50.47^o} \hfill \\
C = {180^o} – {50.47^o} = {129.53^o} \hfill \\
\end{gathered} \]
To find Angle B
\[\begin{gathered}
B = {180^o} – {40^o} – {129.53^o} \hfill \\
B = {10.47^o} \hfill \\
\end{gathered} \]
TO find the length of side b
\[\begin{gathered}
\frac{b}{{\sin B}} = \frac{a}{{\sin A}} \hfill \\
\frac{b}{{\sin 10.47}} = \frac{5}{{\sin 40}} \hfill \\
b = \frac{5}{{\sin 40}} \times \sin 10.47 \hfill \\
b = 1.414cm \hfill \\
\end{gathered} \]