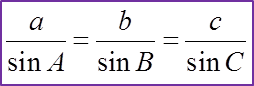9.1 The Sine Rule
In a triangle ABC in which the sides BC, CA and AB are denoted by a, b, and c as shown, and A, B, C are used to denote the angles at the vertices A, B, C respectively,
The sine rule can be used when
(i) two sides and one non-included angle or
(ii) two angles and one opposite side are given.
(A) If you know 2 angles and 1 side ⇒ Sine rule
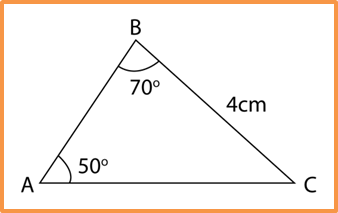
Example:
Calculate the length, in cm, of AB.
Solution:
∠ACB = 180o – (50o + 70o) = 60o
(B) If you know 2 sides and 1 angle (but not between them) ⇒ Sine rule
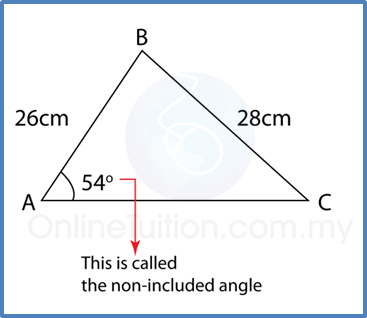
Example:
Calculate ∠ACB.
Solution:
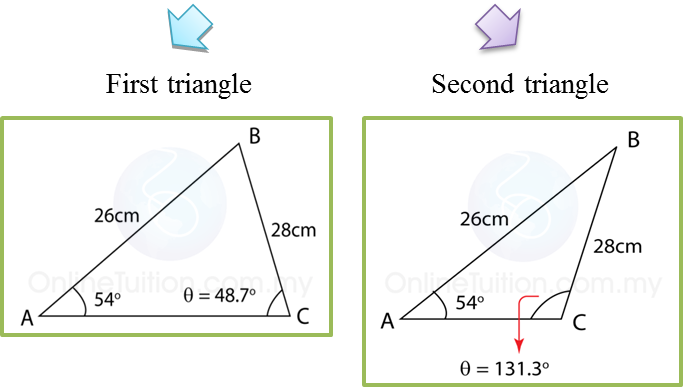
(C) Case of ambiguity (2 possible triangles)
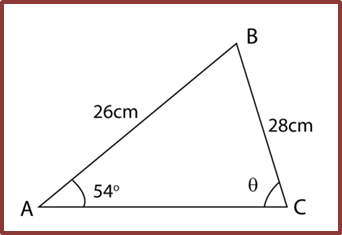
Example
Calculate ∠ACB, θ.
Solution:
Two possible triangle with these measurement
AB = 26cm BC = 28 cm Ð BAC = 54o